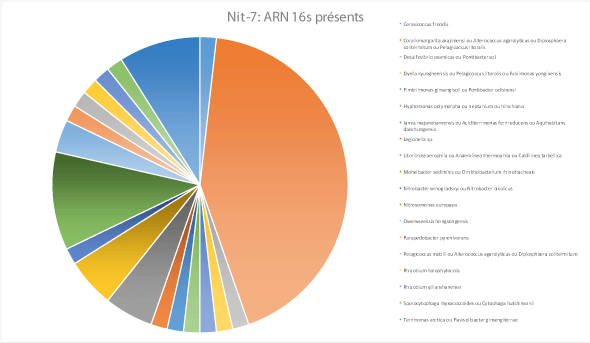
16s rRNA gene identification from 3 environmental samples @ Private company
PCR Success Story #18Project Description
16s rRNA gene identification and quantification of bacterial diversity from 3 environmental bacterial populations maintained in industrial bioreactors (paid service)
This 16s rRNA gene identification project originated from a customer from a cold sales call performed at the main location of a private company located near our own main office located on the south shore of Montreal. The company had previously performed a similar identification of 2 consortiums about 5 years ago using a similar method. To verify the potential population drift over 5 years of the bacterial cultures maintained in their bioreators, they constracted us to identify and quantify the bacterial diversity of 3 consortiums of mixed bacteria (originally obtained from environmental sources) using up-to-date 16s rRNA gene identification methodologies.
This project contained many methodological steps
- gDNA extraction from the 3 bacterial populations using an optimized kit for both Gram- and Gram+ cell lysis;
- High-Fidelity amplification of 16s rRNA gene using ‘truly universal’ primers to maximize bacterial specie identification;
- Cloning of amplified fragments into a topoisomerase-based vector that eliminates blue/white colony screening;
- Colony DNA extraction using an advanced, yet simple, DNA extraction reagent.
- Colony PCR using M13 primers
- Sequencing
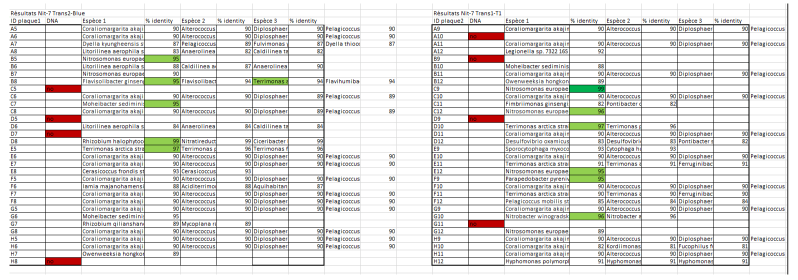
- BLASTn analysis or 16s rRNA sequences (performed on November 27th, 2016)
Note: this is a paid service. We try our best to give as much detailed information to the readers, yet preserve the critical data to protect intellectual property of the customer.
Project Details
Client: Private Company located on the south shore of Montreal
Date: November 27th, 2016
Type of experiment: Gram+/- gDNA extraction, High-Fidelity multiplex PCR, pEASY topoisomerase cloning, Colony DNA extraction and PCR.
DNA Polymerase: 2x TransStart® FastPfu (High-Fidelity) PCR SuperMix
Competitor: none
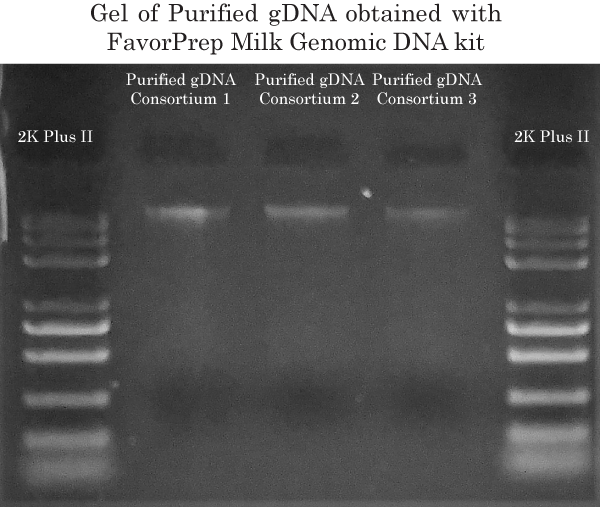
Gram- / Gram+ gDNA extraction
To extract the genomic DNA from both Gram+ and Gram- bacteria contained in the 3 consortiums, we have used the FavorPrep™ Milk Bacterial DNA Extraction Kit because the bacterial cell lysis is performed in 2 separate steps. Step 1 provides efficient cell lysis using Proteinase K. Step 2 provides efficient cell lysis using lysosyme. Using this 2-step cell lysis protocol enabled us to extract gDNA from a maximum of different bacterial species in order to perform 16s rRNA gene identification in subsequent steps.
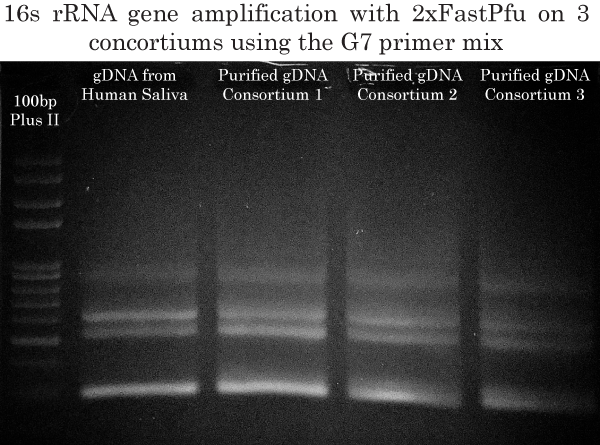
16s rRNA High-Fidelity Multiplex Amplification using the G7 primer mix
In order to maximize the identification of all bacterial species present in all three consortiums, we used the G7 primer mix and 2xTransStart FastPfu (High-Fidelity) PCR Supermix to amplify the 16s rRNA gene from our purified gDNAs obtained previously. In his 2011 paper, Dr Barghouthi has successfully identified 101/101 of bacterial isolates using the G7 mix (Golden mixture 7). The G7 mix was therefore ideal for our 16s rRNA identification project. Also, the G7 mix allows for PCR amplification at higher annealing temperatures than with previously published primers, thereby increasing specificity.
The DNA in the 700 bp to 1100 bp rage was gel extracted and purified using the FavorPrep GEL/PCR Purification Kit.
PCR setup for 16s rRNA amplification
- H2O: 13.4 ul
- 2x TransStart FastPfu Supermix: 15 ul
- G7 primer mix (10 uM each): 0.6 ul
- gDNA (30 ng/ul): 1 ul
PCR cycling for 16s rRNA amplification
- Initial denaturation: 90s at 95°C
- 32 cycles:
- 15s at 95°C
- 30s at 57°C
- 30s at 72°C
- Final extension: 180s at 72°C.
Cloning into pEASY -Blunt Zero
The 700bp to 1100bp that was purified using the FavorPrep GEL/PCR Purification Kit was cloned using topoisomerase-based cloning into pEASY-Blunt Zero vector and transformed in parallel in Trans2-Blue and Trans1-T1 phage resistant chemically competent cells. Briefly, 2 ul of each purified DNA was mixed with 1 ul of pEASY-Blunt Zero at 37°C for 20 minutes and transformed in competent cells. Rescued cells were plated on Ampicilin selective LB-agar plates.
The pEASY-Blunt Zero vector has the advantage of eliminating blue/white colony screening by interupting the lethal ccdB gene. Un-cloned vectors express ccdB and prevent colony growth on selective media.
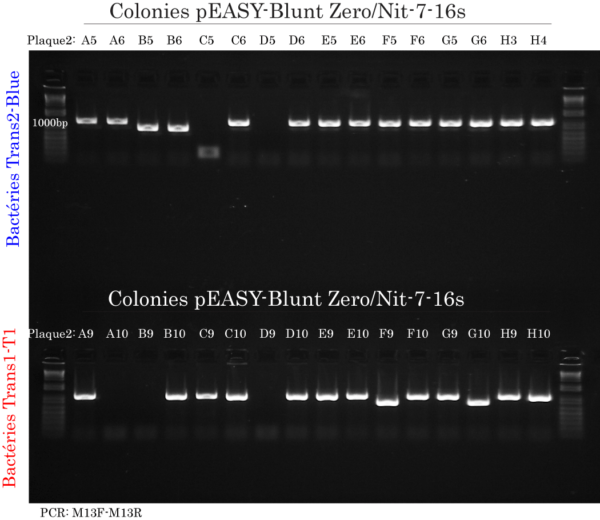
Colony DNA extraction & PCR
Instead of performing plasmid DNA minipreps, we used colony PCR to amplify the cloned 16s rRNA gene DNA from pEASY-Blunt Zero using M13 forward and reverse primers provided with the pEASY-Blunt Zero Cloning Kit.
Briefly, DNA from 96 Trans2-Blue (32 from each consortium) and 96 Trans1-T1 phage resistant cells (32 from each consortium) was extracted using a new, quick and innovative extraction reagent (available soon) much more efficient than water or other reagents used for traditional colony PCR. Then, 0.5 ul of extracted DNA was amplified using 2x TransTaq®-T PCR SuperMix (+dye) which provided fidelity and ready-to-load dye for convenience.
The gel image represented here is from 1 of the 3 consortiums where colony PCR was performed on Trans2-Blue or Trans1-Ti colonies.
Want Us to take Good Care of your Project?
Put us in charge of your project!