GC-rich PCR: Comparison of FastPfu FLY and Q5 High-Fidelity DNA Polymerases
Amplification of human ARX from gDNAGC-rich PCR: FastPfu FLY vs Q5® High-Fidelity DNA Polymerase
GC-rich PCR can be difficult to achieve
Our aim was to verify compare FastPfu FLY (TransBionovo) and Q5 (NEB) high-fidelity DNA Polymerase at amplifying a GC-rich sequence (human ARX; 79% GC) from purified human genomic DNA. GC-rich PCR often requires the addition of different molecules to PCR reactions to act as DNA ‘looseners’. FastPFu FLY uses a compound named PCR Stimulant. Q5® (M0491 from NEB) uses a GC enhancer. According to our sense of smell (yes we smelled them), both are different in composition.
Q5 is a registered trademark of New England Biolabs, Inc.
Our target: Human Aristaless-Related Homeobox (ARX) exon 2
Aristaless-Related Homeobox) exon 2 containing 2 polyalanine tracts. Alanine tracts are coded by imperfect trinucleotide repeats (GCN), among which GCG is significantly over-represented in the polyalanine coding sequence (5). It is stable during both meiosis and mitosis (6). However, polymorphisms in length are frequent involving more than 30% of tracts longer than seven alanines and correlating with the length of both the overall tract and the number of a single codon in a row (5). More details can be found here.
GC-rich PCR conditions for ARX:
We’ve previously described the successful amplification of ARX from pure and unpurified gDNA using FastPfu and FastPfu FLY. These previous results served as guidelines for the present annealing temperatures (Ta) used herein, concentrations of PCR stimulant and primer concentration.
In an attempt to compare FastPfu FLY to Q5® High-Fidelity DNA Polymerase (M0491 from NEB), we varied the final concentrations (0x, 1.7x or 2.3x) of PCR Stimulant (for FastPfu FLY) or GC enhancer (for Q5), and primer concentrations used with both enzymes. Primer concentrations used with Q5 were kept constant at 0.4 nM close to the recommendations of the manufacturer, which are of 0.5 nM for each primer.
Details
Date: November 26-28th, 2016
Type of experiment: High-Fidelity GC-rich PCR from human gDNA
DNA Polymerase: TransStart FastPfu FLY (Ultra-HiFi) DNA Polymerase
Competitors: NEB Q5® High-Fidelity DNA Polymerase M0491
PCR reaction setup for GC-rich PCR
- H2O : fill to 15 ul
- 5x buffer : 3 ul
- dNTPs (2.5 mM): 1.2 ul (0.2 mM final)
- Forward primer (10 uM): 0.3 ul (0.2 nM final) OR 0.6 ul (0.4 nM final)
- Reverse primer (10 uM) : 0.3 ul (0.2 nM final) OR 0.6 ul (0.4 nM final)
- gDNA : 1.5 ul (15 ng)
- FastPFu FLY (2.5 u/ul) or Q5 (2 u/ul) : 0.3 ul or 0.15 ul respectively
- PCR Stimulant or GC enhancer: 0, 5 or 7 ul (0x, 1.27x or 2.3x final) of each matching their polymerase.
Reactions were set up on ice because the Q5 version M0491 is not a hotstart DNA polymerase.
PCR cycling for human ARX exon 2, 658 bp (79% GC):
- Denaturation: 60s at 98 °C
- 35 x
- Denaturation: 15s at 98 °C
- Annealing: 15s at 51 or 53 °C
- Extension: 20s at 68 °C
- Final extension: 120s at 68 °C
DNA sequence of human ARX exon 2, 658 bp (79% GC):
ccaaggcgtcgaagtctggtggtgcgcggtccccgcacgcctgggcctaggcactgggggagcaactgcgggcgggccccggcagcagccctggctgggactccccggccggccggctggctgatagctctcccttgcccgcaggctcccctaagagcagcagcgccccgttcgaggccgagctgcacctgccgcccaagctgcggcgcctgtacggcccgggcgggggccgcctccttcagggtgcggcagcggcggcggcggcggcggcggcggcggcggcagcggccgccacggccacggcgggtccacgcggggaggcccctccgccgccaccgccaaccgcgcggcccggggaacggccggacggcgcaggggccgccgcggcagccgcggccgcggccgccgcggcctgggacacgctcaagatcagccaggcgccgcaggtgagcatcagccgcagcaagtcgtaccgcgagaacggggcgcccttcgtgccgccgccgcccgcgctggacgagctgggcggcccggggggcgtcacgcacccggaggagcgcctcggcgtggccggcggcccgggcagcgccccggctgcgggtggtggcaccggcaccgaggacgacgaggaggagctgctggaggacgaagaagatga
Poly-alanine tracts, GC(N) repeats are indicated in bold and red color.
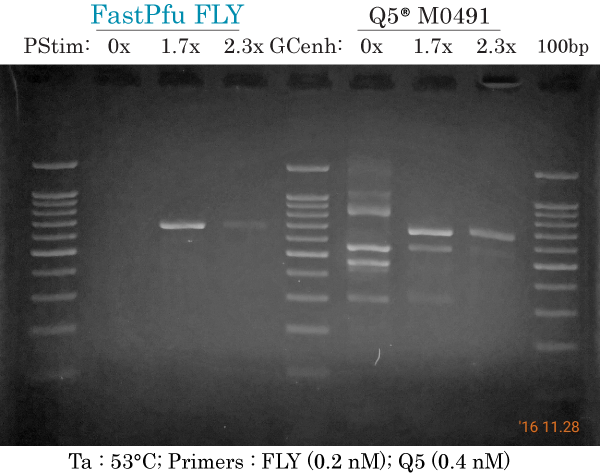
53°C & low primers (FLY)
PCR amplification of human ARX 658 bp at Ta 53°C using low primers (0.2 nM each) for FastPfu FLY and high primers (0.4 nM each) for Q5 using a gradient of PCR Stimulant (PStim) of GC enhancer (GCenh) for each DNA polymerase.
FastPfu FLY:
- 0x : did not produce non-specific bands without PCR Stimulant
- 1.7x : most intense and specific 658 bp band
- 2.3x : specific but less intense
Q5:
- 0x : at least 5 non-specific bands and no specific band at 658 bp.
- 1.7x : 2 non-specific bands that are less intense than the specific band
- 2.3x : 1 non-specific band plus specific band at 658 bp.
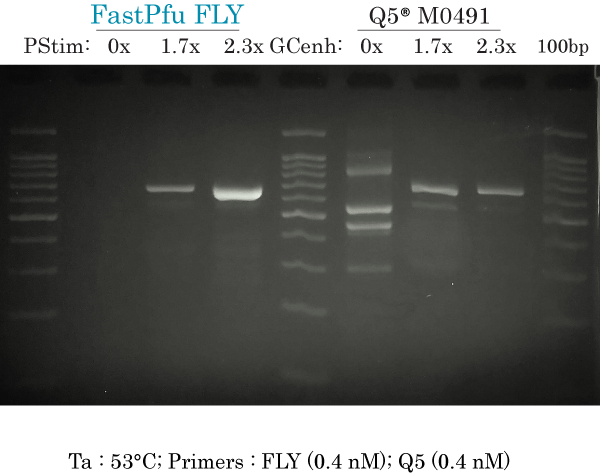
53°C & high primers (FLY)
PCR amplification of human ARX 658 bp at Ta 53°C using high primers (0.4 nM each) for both FastPfu FLY and Q5 using a gradient of PCR Stimulant (PStim) of GC enhancer (GCenh) for each DNA polymerase.
FastPfu FLY:
- 0x : did not produce non-specific bands
- 1.7x : intense and specific band, with ‘ghost-like’ very faint non-specific band at approximately 600 bp (very similar to 0.2 nM condition). Some very faint smear can be seen in the range of 200-400 bp.
- 2.3x : Very intense specific band. Very faint non-specific band at approximately 600 bp (very similar to Q5). Some very faint smear can be seen in the range of 200-400 bp.
Q5:
(different PCR reaction than previous data, but same results as previous data because of same conditions)
- 0x : at least 5 non-specific bands and no specific band at 658 bp.
- 1.7x : 2 non-specific bands that are less intense than the specific band
- 2.3x : 1 non-specific band plus specific band at 658 bp.
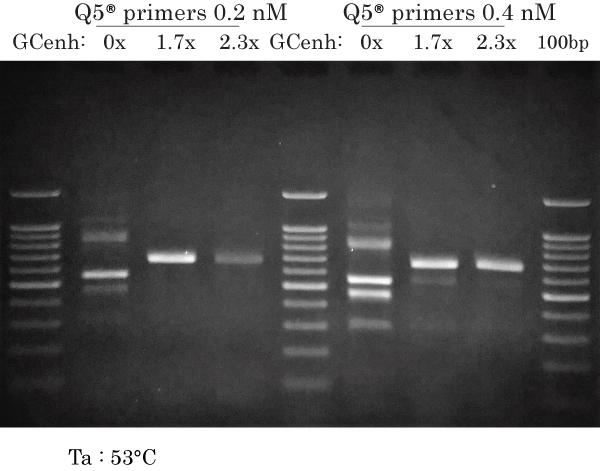
53°C & low vs high primers (Q5 only)
PCR amplification of human ARX 658 bp at Ta 53°C using low (0.2 nM) or high primers (0.4 nM each) for Q5 using a gradient of GC enhancer (GCenh).
Q5 (0.2 nM):
- 0x : same non-specific bands as with 0.4 nM primers, but less intense
- 1.7x : intense and specific band (best condition for Q5)
- 2.3x : specific band only
Overall, very similar pattern to FastPfu FLY with Ta 53°C and 0.2 nM primers, at the exception of the 5 non-specific bands present without GC enhancer obtained with Q5.
Q5 (0.4 nM):
Different PCR reaction than previous data, but same results as previous data because of same conditions (at Ta 53°C).
The manufacturer recommends using 0.5 nM of each primer. Our results indicate that the product recommendation for Q5 M0491 should be omitted in the present example nad using 0.2 nM of each primer is optimal under our experimental conditions.
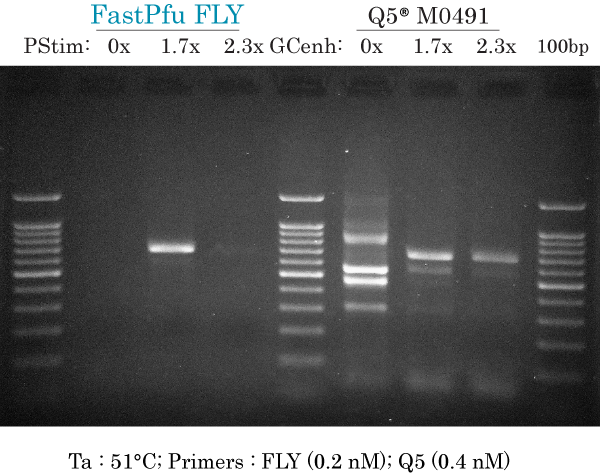
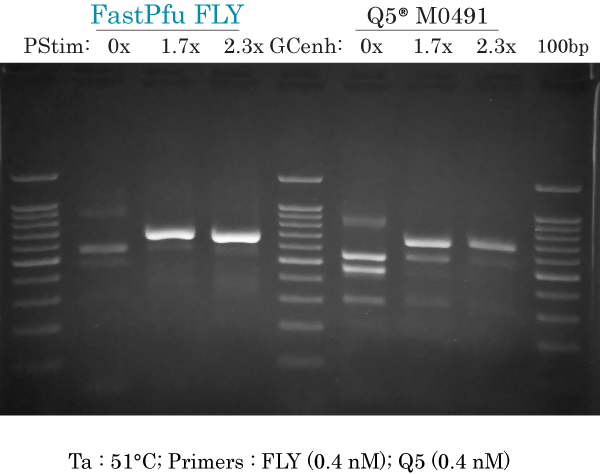
51°C & low primers (FLY)
PCR amplification of human ARX 658 bp at Ta 51°C using low primers (0.2 nM each) for FastPfu FLY and high primers (0.4 nM each) for Q5 using a gradient of PCR Stimulant (PStim) of GC enhancer (GCenh) for each DNA polymerase.
FastPfu FLY:
- 0x : did not produce non-specific bands without PCR Stimulant
- 1.7x : intense and specific 658 bp band, with very faint non-specific band approximately at 600 bp. Small amount of smearing above the 658 bp band
- 2.3x : specific but much less intense
Q5:
- 0x : at least 5 non-specific bands, no specific band at 658 bp and smearing throughout the lane
- 1.7x : 2 non-specific bands that are less intense than the specific band. Small amount of smearing above the 658 bp band
- 2.3x : 1 or 2 non-specific bands plus specific band at 658 bp. Small amount of smearing above the 658 bp band.
51°C & high primers (FLY)
PCR amplification of human ARX 658 bp at Ta 51°C using high primers (0.4 nM each) for both FastPfu FLY and Q5 using a gradient of PCR Stimulant (PStim) of GC enhancer (GCenh) for each DNA polymerase.).
Despite resulting in highly intense specific bands using 1.7x or 2.3x PCR Stimulant, these PCR conditions were not ideal for FastPfu FLY because the 0x PCR Stimulant condition started to show the same pattern of non-specific bands as obtained with Q5, but with much lesser intensity.
Conclusion
Our conclusion is that we were able to amplify human ARX exon 2 from purified human gDNA using either FastPfu FLY and Q5 DNA polymerases, with the help of PCR Stimulant or GC enhancer.
FastPfu FLY was easier to work with because we could follow the manufacturer’s recommendations, whereas we had to tune things up for Q5 from NEB.
FastPfu FLY overall produced much less non-specific amplication than its counterpart. Most amplicons were pure and specific with near-neglectable (difficult to see) and occasional non-specific bands, at the exception of the low annealing temperature and high primer concentration condition.
Which polymerase will you choose for your next GC-rich PCR?
Are you Ready to FLY?
DNA Polymerase Comparison Chart
Specifications and pricing of commercially available Taq DNA Polymerases and High-Fidelity DNA Polymerases in Canada.
Detection Limit of High-Fidelity DNA Polymerases on gDNA
Published on Jan 30, 2017 by Simon Roy, Ph.D Detection Limit of High-Fidelity DNA Polymerases using Human gDNA for Template We previously determined the detection limit of different Taq DNA Polymerases using human genomic DNA as a template for PCR. For this instance,...
PCR Purification Kit Comparison - DNA Clean Up
Which is the Best Kit for DNA Clean Up? Our aim was to perform a PCR Purification Kit Comparison from different vendors. At Civic Bioscience, we distribute the Favorprep™ and EasyPure® product lines from FAVORGEN and TransBionovo respectively. First, the FavorPrep™...
miniPCR Review : How I use a portable PCR thermocycler to help life scientists day-to-day.
The miniPCR and blueGel systems represent the core instruments involved in the assistance we provide to real scientists who conduct life science research in Canada. Both laboratory instruments were essential in solving dozens of problems that prospect customers were...
Detection Limit of Taq DNA Polymerase
What's the Detection Limit of Taq ? How many DNA copies from gDNA? There are MANY Taq DNA Polymerases out there on the market. Some are driven by strong marketing and others by strong performance. Our aim was to verify the Detection Limit of Taq DNA Polymerases in PCR...
Taq DNA Polymerase Comparison (Part 2)
Taq DNA Polymerase Comparison...which one should you choose? Nowadays, many suppliers offer Taq DNA Polymerases. Our aim was to perform a Taq DNA Polymerase Comparison. Our Taq DNA Polymerase Comparison assay consisted in PCR amplification of a fragment of the human...